随机对照试验(randomized controlled trial,RCT)是评估治疗、预防、干预效果的最佳研究,但低质量的RCT会错误估计疗效。因此,应当准确、完整地报告RCT的设计、实施、分析和外部有效性信息,从而让读者能够判断试验的内部和外部有效性。本文主要介绍RCT的报告规范——临床试验报告的统一标准(consolidated standards of reporting trials,CONSORT)概述。
关键词:随机对照试验; 报告规范; 临床试验报告的统一标准; CONSORT
一、RCT报告规范背景
RCT报告的质量与研究结果的可信度有关,低质量的RCT可能造成偏倚。为了进一步规范RCT报告,1996年,由临床试验人员、统计学家、流行病学家和生物医学编辑组成的国际小组制定并发表了临床试验报告的统一标准(consolidated standards of reporting trials,CONSORT),即CONSORT声明。1999年,CONSORT声明被修订,修订后的声明包括1份含22个条目的清单和1张流程图。并且CONSORT组织还制定了一份解释文件对清单中各个条目的含义和依据进行详细说明。2010年,CONSORT组织根据最新的方法学证据再次更新了清单、流程图和解释文件,更新后的清单由25个条目组成,解释文件说明了每个条目纳入清单的理由、方法学背景和已发表的报告实例。
目前,越来越多的国际学术期刊以要求作者应按照CONSORT声明准备稿件,包括Lancet、British Medical Journal、Journal of American Medical Association 和Annals of Internal Medicine等国际顶尖期刊;并且越来越多的生物医学期刊编辑组织也对CONSORT声明表示了支持,包括国际医学杂志编辑委员会、科学编辑委员会、世界医学编辑协会等。
二、CONSORT扩展版
CONSORT声明主要适用于严格的两平行组设计,但不同的临床试验在设计、干预措施和结局指标等方面会有所不同,为了进一步提高这些试验的报告质量,CONSORT组织扩展和修改了CONSORT声明,以便不同的临床试验应用,即CONSORT扩展版。主要包括了以下版本:
- 整群随机对照试验(cluster randomised trials)
- 非劣效性和等效性随机对照试验(noninferiority/equivalence randomized trials)
- 实效性随机对照试验(pragmatic randomized controlled trials, PRCT)
- 适应性设计随机对照试验(adaptive design randomized trials)
- 随机对照交叉临床试验(randomised crossover trials)
- 单病例随机对照试验(n-of-1 trial)
- 探索研究和可行性研究(randomised pilot and feasibility trials)
- 针灸临床试验(acupuncture trials)
- 中医药随机对照试验(traditional Chinese medicine randomized trials)
- 中草药干预随机对照试验(herbal medicinal interventions randomized trials)
- 非药物干预临床试验(non-pharmacologic treatment interventions randomized trials)
- 社会心理学干预的随机对照临床试验(randomised trials of social and psychological interventions)
- 患者报告结局临床试验(patient reported outcome trials)
- 随机对照试验中的不良事件(adverse event in randomized trials)
- 涉及人工智能干预的临床试验(clinical trials with artificial intelligence intervention)
- 随机对照试验的摘要(abstract of randomized trials)
本文着重介绍CONSORT 2010声明的清单条目,具体内容可参考CONSORT声明官方网站(http://www.consort-statement.org),以下内容是对相关内容的理解与汇总,感兴趣的读者请以官方文件为主。
三、CONSORT报告条目清单及流程图
(一) CONSORT报告条目清单
表1 随机平行对照试验CONSORT 2010的清单条目的中英文对照
| 内容 | 条目序号 | 条目内容 |
| Title and abstract 标题与摘要 | 1a | Identification as a randomized trial in the title 在题目中体现随机化试验 |
| 1b | Structured summary of trial design, methods, results, and conclusions (for specific guidance see CONSORT for abstracts) 结构化摘要,包括试验设计、方法、结果和结论(详见CONSORT摘要) | |
| Introduction 引言 | ||
| Background and objectives 背景和目的 | 2a | Scientific background and explanation of rationale 研究的科学背景和试验的理由 |
| 2b | Specific objectives or hypotheses 研究目的或假设 | |
| Methods 方法 | ||
| Trial design 试验设计 | 3a | Description of trial design (such as parallel, factorial), including allocation ratio 描述试验设计(如平行、析因设计),包括分配比例 |
| 3b | Important changes to methods after trial commencement (such as eligibility criteria), with reasons 试验开始后方法上的重要改变(如纳入排除标准)及原因 | |
| Participants 研究对象 | 4a | Eligibility criteria for participants 研究对象的纳入排除标准 |
| 4b | Settings and locations where the data were collected 数据收集的机构和地点 | |
| Interventions 干预 | 5 | The interventions for each group with sufficient details to allow replication, including how and when they were actually administered 各组干预的详细内容,包括何时、如何实际开展,以便能够重复 |
| Outcomes 结局 | 6a | Completely defined pre-specified primary and secondary outcome measures, including how and when they were assessed 完整明确地定义预先规定的主要和次要结局指标,包括何时、如何评价 |
| 6b | Any changes to trial outcomes after the trial commenced, with reasons 试验开始后结局的改变及原因 | |
| Sample size 样本量 | 7a | How sample size was determined 样本量如何确定 |
| 7b | When applicable, explanation of any interim analyses and stopping guidelines 对期中分析和中止试验的条件、时间进行解释(如适用) | |
| Randomization 随机化 | ||
| Sequence generation 序列生成 | 8a | Method used to generate the random allocation sequence 产生随机分配序列的方法 |
| 8b | Type of randomization; details of any restriction(such as blocking and block size) 随机化类型;任何限定情况的详细信息(如区组和区组大小) | |
| Allocation concealment mechanism 分配隐藏机制 | 9 | Mechanism used to implement the random allocation sequence (such as sequentially numbered containers), describing any steps taken to conceal the sequence until interventions were assigned 实施随机序列的方法(如连续编码的容器),阐明隐藏分配序列的措施 |
| Implementation 实施 | 10 | Who generated the random allocation sequence who enrolled participants,and who assigned participants to interventions 产生分配序列、纳入研究对象、分配研究对象的人员 |
| Blinding 盲法 | 11a | If done, who was blinded after assignment to interventions ( for example, participants.care providers,those assessing outcomes ) and how 如果实施了盲法,应说明对谁设盲(如研究对象、干预提供者、结局评价者),如何实施的 |
| 11b | If relevant, description of the similarity of interventions 组间干预的相似性 | |
| Statistical methods 统计方法 | 12a | Statistical methods used to compare groups for primary and secondary outcomes 组间比较,主要结局与次要结局的统计方法 |
| 12b | Methods for additional analyses, such as subgroup analyses and adjusted 其他分析方法,如亚组分析和校正分析 | |
| Results 结果 | ||
| Participant flow (a diagram is strongly recommended 研究对象纳入流程(强烈推荐流程图) | 13a | For each group, the numbers of participants who were randomly assigned, received intended treatment,and were analyzed for the primary outcome 各组接受随机分配、接受干预和进入主要结局分析的研究对象数量 |
| 13b | For each group, losses and exclusions after randomization, together with reasons 各组随机化之后发生的脱落或失访、排除,以及原因 | |
| Recruitment 研究对象的招募 | 14a | Dates defining the periods of recruitment and follow-up 招募研究对象和随访的日期范围 |
| 14b | Why the trial ended or was stopped 研究结束或停止的原因 | |
| Baseline data 基线数据 | 15 | A table showing baseline demographic and clinical characteristics for each group 反映各组基线人口学特征和临床特征的表格 |
| Number analyzed 分析数量 | 16 | For each group, number of participants (denominator) included in each analysis and whether the analysis was by original assigned groups 各组纳入分析的研究对象数量(分母),是否按照最初分组进行分析 |
| Outcomes and estimation 结局和效应估计 | 17a | For each primary and secondary outcome, results for each group, and the estimated effect size and its precision (such as 95% confidence interval) 对每个主要和次要结局,报告各组结果、效应估计和精确度(如95%置信区间) |
| 17b | For binary outcomes presentation of both absolute and relative effect sizes is recommended 对二分类结局,报告绝对效应和相对效应 | |
| Ancillary analyses 其他分析 | 18 | Results of any other analyses performed, including subgroup analyses and adjusted analyses, distinguishing prespecified from exploratory 报告其他分析(包括亚组分析和校正分析)结果,区分预先设定的分析和探索性分析 |
| Harms 损害 | 19 | All important harms or unintended effects in each group 所有重要损害或未预期到的效应 |
| Discussion 讨论 | ||
| Limitations 局限性 | 20 | Trial limitations; addressing sources of potential bias; imprecision; and, if relevant, multiplicity of analyses 试验局限性;关注偏倚的来源;不精确程度;多重比较问题 |
| Generalizability 外推性 | 21 | Generalizability (external validity, applicability) of the trial findings 试验结果的外推性(外部有效性、适用性) |
| Interpretation 结果解释 | 22 | Interpretation consistent with results, balancing benefits and harms, and considering other relevant evidence 权衡收益和损害,并考虑其他相关证据,对结果进行解释 |
| Other information其他信息 | ||
| Registration 注册 | 23 | Registration number and name of trial registry 注册机构与注册号 |
| Protocol 研究方案 | 24 | Where the full trial protocol can be accessed, if available 可以获得完整研究方案的地方 (如适用) |
| Funding 资助 | 25 | Sources of funding and other support(such as supply of drugs), role of funders 资助来源和其他支持,资助者的作用 |
(二) CONSORT报告流程图
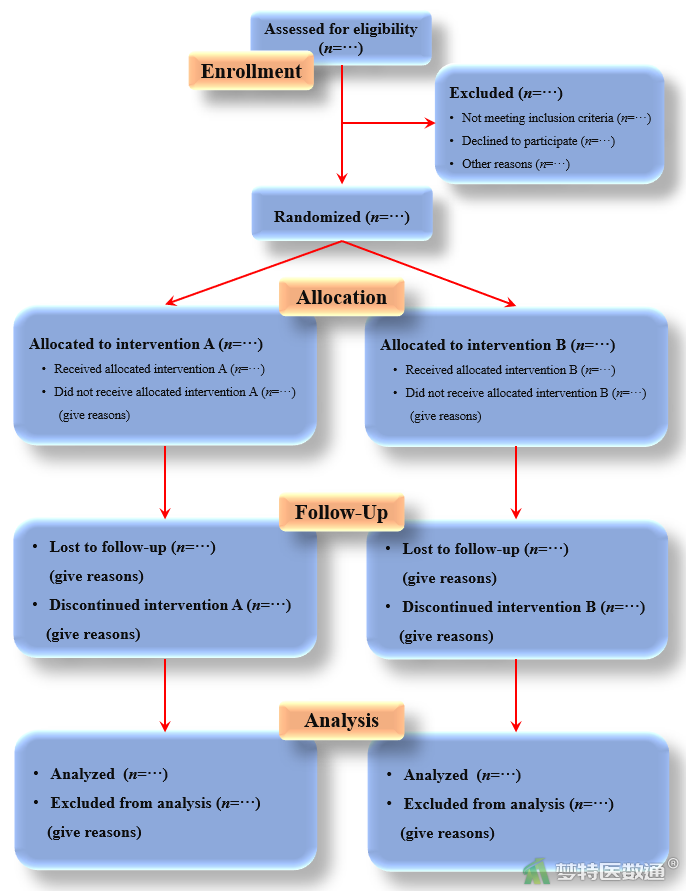

四、CONSORT清单使用注意事项
CONSORT声明是报告RCT的最低限度的建议,当期刊要求按照CONSORT声明准备稿件时,建议投稿时附上检查表(checklist)并注明每个条目在文章哪一页提及。但这并不意味着所有RCT报告格式均标准化,作者在使用CONSORT时应按照期刊的要求和所研究内容的具体情况详尽清楚地报告具体条目即可。此外,值得注意的是,CONSORT声明并不是临床科研设计的指南,只是规范RCT报告或文章撰写的标准性文件,并不包含任何对试验设计、实施和结果分析的建议,使用CONSORT声明对RCT研究进行质量评价也是不合适的。但CONSORT声明的广泛传播和采用显然间接影响了RCT研究的方法学质量,因为研究者为了增加论文发表的机会,会从一开始就更加重视研究设计和实施的方法学质量。
注:本文内容是参考相关文献后对PRCT CONSORT扩展版报告规范原文的概述,仅代表本网站观点。关于随机平行对照试验CONSORT声明的更多内容详见官方网站(http://www.consort-statement.org)或论文CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2844940/)、CONONSORT 2010 Explanation and Elaboration: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials (https://www.bmj.com/content/340/bmj.c869)。